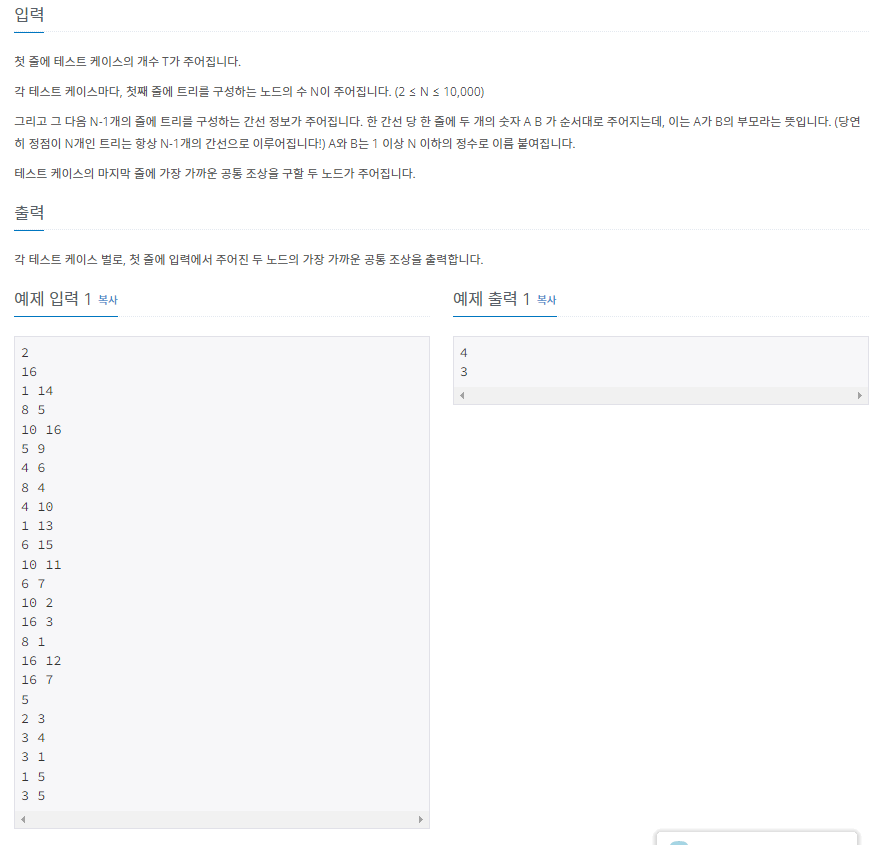
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/3584
3584번: 가장 가까운 공통 조상
루트가 있는 트리(rooted tree)가 주어지고, 그 트리 상의 두 정점이 주어질 때 그들의 가장 가까운 공통 조상(Nearest Common Anscestor)은 다음과 같이 정의됩니다. 두 노드의 가장 가까운 공통 조상은, 두
www.acmicpc.net

해당 문제는 LCA (최소 공통 조상) 문제이다!
LCA 알고리즘 개념 출처: https://www.crocus.co.kr/660
* LCA 알고리즘이란?
- 최소 공통 조상을 찾는 알고리즘
- 두 정점 u, v(혹은 a, b)에서 가장 가까운 공통 조상을 찾는 과정
* LCA 알고리즘 과정
1. 모든 노드
에 대해 깊이를 구한다.
2. 모든 노드에 대해 2^i 번째 부모를 구한다.
3. 두 노드의 깊이가 동일하도록 거슬러 올라간다.
4. 같은 조상 노드가 나올 때까지 맨 위에서부터 내려온다 (지수적으로)
코드 출처: https://ghqls0210.tistory.com/135
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int t, n;
vector<int>tree[10001];
bool check[10001];
int Log = 14;
int parent[10001][14];
// parent[i][j] : i번 노드의 2^j번째 부모, 2^13<10000<2^14
// parent[i][j] = parent[parent[i][j-1]][j-1] 만족
int depth[10001]; // 노드의 depth 구하기
int node1, node2;
int find_root[10001]; // 루트 노드 찾기용
void make_tree()
{
// 트리 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < 10001; i++) {
tree[i].clear();
check[i] = false;
memset(parent[i], sizeof(parent[i]), 0);
depth[i] = -1;
find_root[i] = 0;
}
// 트리 입력
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
tree[a].push_back(b);
tree[b].push_back(a);
find_root[b] = a;
}
// 구할 노드 입력
cin >> node1 >> node2;
}
// node의 바로 윗부분과 연결 및 depth구하기
void dfs(int node, int Depth)
{
check[node] = true;
depth[node] = Depth;
for (int i = 0; i < tree[node].size(); i++) {
int next_node = tree[node][i];
if (check[next_node] == false) {
parent[next_node][0] = node;
dfs(next_node, Depth + 1);
}
}
}
// 루트 노드 구하기
// 원래 트리는 루트 아무거나 해도 상관없지만 문제에서 부모가 주어졌으므로
// 루트를 구해서 set_parent 돌리기
int Find_root()
{
for (int node = 1; node <= n; node++)
if (find_root[node] == 0)
return node;
}
// 전체 부모 관계 설정
void set_parent(int root)
{
dfs(root, 0); // 루트 노드 root, 루트 노드의 depth=0
for (int jump = 1; jump < Log; jump++) {
for (int node = 1; node <= n; node++) {
parent[node][jump] = parent[parent[node][jump - 1]][jump - 1];
}
}
}
int LCA(int node1, int node2)
{
// node2가 더 깊게 있는 것으로 설정
if (depth[node1] > depth[node2])
swap(node1, node2);
// 두 노드의 깊이 동일하도록 설정
for (int i = Log - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (depth[node2] - depth[node1] >= (1 << i)) {
node2 = parent[node2][i];
}
}
// 부모 같은 경우 찾기
if (node1 == node2)
return node1;
for (int i = Log - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (parent[node1][i] != parent[node2][i]) {
node1 = parent[node1][i];
node2 = parent[node2][i];
}
}
return parent[node1][0];
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
make_tree();
int root = Find_root();
set_parent(root);
cout << LCA(node1, node2) << '\n';
}
}'Algorithm > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm][C언어] 백준 15059번: Hard choice (0) | 2022.10.07 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm][C언어] 백준 11653번: 소인수분해 (0) | 2022.10.05 |
| [Algorithm][C언어] 백준 2033번: 반올림 (0) | 2022.09.27 |
| [Algorithm][C언어] 백준 17009번: Winning Score (1) | 2022.09.26 |
| [Algorithm][파이썬] 백준 2609번: 최대공약수와 최소공배수 (0) | 2022.09.19 |



